Contents
- KCSE Kiswahili Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Kiswahili Paper 2 2010
- KCSE Kiswahili Paper 3 2010
- KCSE Home Science Paper 1 2010
- KCSE History and Government Paper 2 2010
- KCSE History and Government Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Business Studies Paper 2 2010
- KCSE Geography Paper 1 2010
- KCSE English Paper 3 2010
- KCSE English Paper 2 2010
- KCSE Business Studies Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Christian Religious Education Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Biology Paper 3 2010
- KCSE Biology Paper 2 2010
- KCSE Chemistry Paper 3 2010
- KCSE Biology Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010
- KCSE English Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Mathematics Paper 1 2010
- KCSE Mathematics Paper 2 2010
Searching for Free KCSE 2010 Past Papers? Find Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (KCSE) 2010 Past Papers, Download 2010 revision Past Papers Here
KCSE Home Science Paper 3 2010
Find KCSE Home Science Paper 3 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Home Science Paper 3 Past paper
THE TEST
Your mother has been away and you are expecting her back for supper. Using all the ingredients listed below, prepare, cook and present a one dish meal and a dessert for the two of you.
Ingredients:
v Pineapple
v Tomatoes
v Onions
v Pawpaw/mangoes
v Salt
v Ripe bananas
v Potatoes
v Sugar
v Minced meat/soya chunks
v Fat/Oil
v Lemon
v Carrots
PLANNING SESSION 30 MINUTES
Use separate sheets of paper for each task listed below and a carbon paper to make duplicate copies. Then proceed as follows:
1. Identify the dishes and write the recipes;
2. Write down your order of work;
3. Make a list of the foodstuff and equipment you will require.
KCSE Kiswahili Paper 1 2010
Find KCSE Kiswahili Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Kiswahili Paper 1 Past paper
Muda: Saa 1¾
Maagizo
(a) Andika insha mbili. Insha ya kwanza ni ya lazima.
(b) Kisha changua insha moja nyingine kutoka hizo tatu zilizo bakia
(c) Kila insha isipungue manano 400.
(d) Kila insha ina alama 20.
1. Insha ya Lazima
Andika wasifu wa ndugu yako ambaye amepanga hafla ya kuchangisha pesa za kumgharamia masomo ya Chuo kikuu. (alama 20)
2. Eleza hatua zinazochukuliwa na serikali kupambana na ufisadi hapa nchini. (alama 20)
3. “Wakenya hawawezi kuafikia umoja wa kitaifa iwapo wataendelea kutumia lugha zao za kienyeji.”Jadili. (alama 20)
4. Binadamu ni ngamba hakosi Ia kuamba. (alama 20)
KCSE Kiswahili Paper 2 2010
Find KCSE Kiswahili Paper 2 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Kiswahili Paper 2 Past paper
1. UFAHAMU (ALAMA 15)
Soma kifungu kifuatacho kisha ujibu maswali
Suala la mahusiano ya wanadamu katika jamii, uainishaji wake na udhihirikaji wake limewashughulisha wataalamu wa elimu jamii kwa dahari ya miaka. Suala hili huwatafakarisha wataalamu hao kutokana na umuhimu wake katika maisha ya binadamu, Msingi mkuu wa uainishaji wa mahusiano hayo ni kukichuza kipindi cha mahusiano yenyewe. Yapo mahusiano baina ya waja ambayo yanachukua muda mfupi, kwa mfano saa au dakika chache, na mengine ambayo huenda yakachukua miaka ayami.
Mahusiano ya muda mrefu kabisa ni yale yanayojulikana kama mahusiano ya kudumu. Inamkinika kudai kuwa miundo ya kijamii, kisiasa na kiuchumi huweza kuyadhibiti mahusiano hayo kwa kiasi kikubwa. Watu wengi huitakidi kuwa uhusiano uliopo baina ya mtu na jamaa yake utachukua muda mrefu, na kwa hivyo ni uhusiano wa kudumu. Hali hii hutokana na uhalisi kuwa tunahusiana na jamaa zetu kwa kipindi kirefu labda tangu ukembe hadi utu uzima wetu. Uhusiano huu hautarajiwi kuvunjwa na umbali wa masafa baina yetu; tunaendelea kuwasiliana kwa barua au, katika enzi hii ya utandawazi, kwa kutumia nyenzo za teknohama kama mtandao na simu za mkononi, na kudumisha uhusiano wetu wa kijamii. Hata hivyo, inawezekana baadhi ya mahusiano ya kijamii yasiwe ya kudumu. Mathalan, uhusiano uiiopo baina ya mke na mume, na ambao unatarajiwa kuwa wa kudumu au wa kipindi kirefu, unaweza kuvunjwa kwa kutokea kwa talaka. Talaka hiyo inavunja ule uwezekano wa uhusiano wa kudumu unaifumbatwa na sitiari ya pingu za maisha.
Katika ngazi ya pili, mahusiano ya kipindi cha wastani, kuna mahusiano yanayouhusisha marafiki zetu maishani, shuleni au kwenye taasisi zozote zile, majirani zetu. wenzetu katika mwahali mwa kazi, washiriki kwenye sehemu za ibada au za burudani na wenzotu kwenye vyama tofauti na makunci ya kujitolea. Inawezekana kudahili kuwa baadhi ya mahusiano haya, hususan baina ya marafiki na majirani huweza kuwa ya miongo na daima. Hali hii huweza kutegemea muundo na mfumo wa jamii. Kwa mfano, kwa wanajamii wanaoishi kwenye janibu Fulani mahsusi, na kwa miaka tawili bila ya kuhajiri, uhusiano wao na majirani huweza kuwa wa kudumu. Hali hii inasigana na hali iliyoko kwenye maisha ya mjini. Maisha ya mijini yana sifa ya kubadilikabadilika. Isitoshe, kutokana na mfumo wa maisha ya kibepari yameghoshi ubinafsi mwingi. Mawimbi ya mabadiliko na ubinafsi huweza kuumomonyoa ukuta wa uhusiano wa kudumu.
Mwelekeo wa maisha ya siku hizi ya uhamaji kutoka maeneo au viambo walikoishi watu unasababisha kupombojea kwa mahusiano ya kudumu baina yao na majirani zao. Uhusiano kati ya wenza katika mazingira ya kazi unahusiana kwa kiasi Fulani na ule wa majirani. Vimbunga vya ufutwaji kazi, ubadiishaji wa kazi, hali zisizotegemewa na mifumo ya kimataifa pamoja na hata mifumo ya kisiasa huweza kuathiri mshikamano wa wanaohusika kazini.
Kiwango cha mwisho cha mahusiano ni uhusiano wa mpito au wa muda mfupi. Mahusiano ya aina hii hujiri katika muktadha ambapo pana huduma Fulani. Huduma hizi zinaweza kuwa za dukani, kwenye sehemu za ibada, kwenye kituo cha mafuta, kwa kinyozi, kwa msusi na kakdhalika. Kuna sababu kadha zinazotufanya kuyazungumzia mahusiano ya aina hii kama ya mpito. Kwanza, uwezekano wa mabadilkio ya anayeitoa huduma hiyo ni mkubwa. Si ajabu kuwa unaporudi kwa kinyozi au msusi unatambua aliyekushughulikia hayupo. Hata hivyo, kuna vighairi hususan pale ambapo mtoa huduma anayehusika ni yule yule mmoja.
Mahusiano ya mpito yanatawaliwa na ‘uhusiano wa chembe chembe.’ Uhusiano wa chembe chembe, bidhaa ya mfumo wa kibepari, unamaanisha kuwa kinachomshughulisha mtu ni chembe ndogo tu ya mwenzake. Chembe hiyo inaweza kuwa huduma, kwa mfano, gazeti analokuuzia mtu, viatu anavyokushonea, nguo anazokufulia, ususi anaokufanyia n.k. Mahusiano ya aina hii yametovukwa na hisia za utu na ni zao !a mifumo ya kisiasa ya kiuchumi na kijamii. Mtu anayehusiana na mwenzake kwa misingi ya chembe ndogo tu, huenda asijali kama mwenzake amekosa chakula, amefutwa kazi, amefiiiwa, ameibiwa na kadhalika.
Suala kuu tunalopaswa kujiuliza ni: je, tunahusiana vipi na jamaa zetu, marafiki zetu na majirani zetu? Je, uhusiano wetu na raia wenzetu ni wa aina gani? Je, uhusiano wetu na nchi yetu ni wa mpito au ni wa kudumu?
(a) Taja kigezo muhimu cha kuzungumzia mahusiano. (alama 1)
(b) Eleza imani ya watu kuhusu uhusiano baina ya jamaa. (alama 1)
(c) Fafanua athari ya teknolojia kwenye mahusiano ya watu. (alama 2)
(d) Eleza sababu nne kuu za kuharibika kwa mahusiano katika maisha ya leo. (alama 4)
(e) Taja sifa kuu ya mahusiano ya muda mfupi. (alama 2)
(f) Je, kifungu hiki kina ujumbe gani mkuu? (alama 2)
(g) Eleza maana ya maneno yafuatayo kama yalivyotumiwa katika kifungu. (alama 3)
(i) inasigana
(ii) yameghoshi
(iii) vighairi
2. MUHTASARI (ALAMA 15)
Jamii ya leo inatawaliwa na kuendeshwa na kanuni ya maarifa. Inawezekana kusema kuwa uchumi wa jamii za leo na zijazo utategemea maarifa zaidi kuliko utakavyotegemey uwezo wowote mwingine. Utambuzi wa uwezo mkubwa wa maarifa katika maisha ya binadamu ndio msingi wa watu kusema ‘maarifa ni nguvu.’
Maarifa huelezwa kwa tamathali hii kutokana na uwezo wa: kuyadhibiti. kuyaendesha, kuyatawala na kuyaongoza maisha ya binadamu popote pale walipo. Mtu ambaye ameyakosa maarifa fulani huwa ameikosa nguvu hiyo muhimu na maisha yake huathirika pakubwa. Kwa msingi huu, maarifa yanaweza kuangaliwa kama utajiri mkubwa ambao binadamu anaweza kuutumia kwa faida yake au kwa faida ya wanajamii wenzake. Ukweli huu ndio unaoelezwa na methali ya Kiswahili: ‘Elimu ni mali’Elimu ni chimbuko la maarifa muhimu maishani.
Msingi wa utajiri na maendeleo ya binadamu popote alipo basi ni maarifa. Je, marifa kwa upande wake yana sifa gani? Maarifa yenyewe hayana upinzani. Maarifa uliyo nayo huweza kuwa na watu wengine wengi pasiwe na upinzani baina yenu kwa kuwa kila mmoja ana maarifa sawa. Kila mmoja ana uhuru wa kuyatumia maarifa hayo kama chanzo cha kuyazalisha maarifa mengine. Utumiaji wa maarifa yenyewe hauyamalizi maarifa hayo. Maarifa hayawezi kugusika ingawa mtu anaweza kuyanyumbua maarifa yenyewe kwa kuyatumia kwa namna tofauti.
Maarifa huingiliana na maarifa mengine. Maarifa aliyonayo mtu mmoja huweza kuhusishwa na maarifa aliyo nayo mtu mwingine ili kuvyaza au kuzuka na maarifa tofauti. Maanfa yanaweza kuchukuliwa kutoka sehemu moja hadi nyingine kwa namna ambavyo mtu hawezi kufanya bidhaa nyingine ile. Kwa mfano, ni muhali mtu kulalamika kuwa hawezi kutembea kutoka sehemu rnoja hadi nyingine kwa sababu ana mzigo mzito wa maarifa kichwani.
Sifa nyingine muhimu ya maarifa ni kuwa yanaweza kuwasilishwa kwa njia za ishara au mitindo mingine ya kidhahania. Ikiwa unataka kukihamisha chombo Fulani kutoka sehemu moja hadi nyingine, lazima uwazie ukubwa wake, uzito wake na labda hata umbal.i wa panapohusika. Maarifa huweza kubadilishwa au kugeuzwa na kuwa ishara ambazo huyafanya kuwasilishwa kwa njia nyepesi kuliko kwa mfano ikiwa mtu atayawasilisha katika muundo wa, kwa mfano, kitabu.
Maarifa yana sifa ya uhusianaji. Kipengele Fulani cha maarifa huwa na maana kinapowekwa sambamba au kugotanishwa na kipengele kingine cha maarifa. Huo huwa muktad’na mzuri wa kueleweka au kuwa na maana. Kw amfano, neno ‘mwerevu’huweza kuwa na inaana kwa kuwekwa katika muktadha wa ‘mjinga”mjanja’, ‘hodari’na kadhalika.
Maarifa huweza kuhifadhiwa katika nafasi ndogo sana. Suala hili linaeleweka kwa njia nyepesi tunapoangalia maarifa katika muktadha wa teknologia. Data zinazowahusu mamilioni ya watu, ambazo zingehitaji maelfu ya maktaba na lukuki ya vitabu, huweza kuhifadhiwa kwenye kifaa kidogo kinachoweza kutiwa mfukoni.
Maarifa hayawezi kudhibitiwa au kuzuiliwa mahali fulani yasisambae. Maarifa hucnea haraka sana. Maarifa ni kitu kinachoepuka pingu za watu wanaopenda kuwadhibiti binadamu wenzao. Hata pale ambapo mfumo wa kijamii au wa kisiasa unafanya juu chini kuwadhibiti raia au watu wenyewe, ni muhali kuyadhibiti maarita yenyewe. Inawezekana kuzidhibiti njia Fulani za ueneaji wa maarifa lakini maarifa hayo yatapata upenyu wa kusambaa. Ni kweli kuwa maarifa ni nguvu inayozishinda nguvu zote.
(a) Fupisha aya ya pili na ya tatu. (maneno 55 – 60) (alama 5, 1 ya utiririko) Matayarisho, Nakala Safi
(b) Eleza sifa kuu za maarifa kama zinavyojitokeza kuanzia aya ya nne hadi aya ya nane. (maneno 100 -110) (alama 10, 2 za utiririko) Matayarisho Nakala Safi
3. MATUMIZI YA LUGHA (ALAMA 40)
(a) Toa mfano wa neno lenye muundo wa silabi ya irabu pekee. (alama 1)
(b) Eleza maana mbili za neno: Barabara. (alama 2)
(c) Sahihisha sentensi:
Abiria walisafiri na ndege. (alama 1)
(d) Tambua na ueleze aina za vivumishi katika sentensi:
Mwanafunzi mkongwe amcpewa tuzo kwa kuwa hodari masomoni. (alama 4)
(e) Andika sentensi ifuatayo katika hali yakinishi.
Usingeacha masomo, usingetaabika vile. (alama 2)
(f) Tunga sentensi ukitumia kielezi cha:
(i) Jumla (alama 1)
(ii) Namna linganisho (alama 1)
(g) Ainisha shamirisho na chagizo katika sentensi:
Vibarua wamefanya kazi haraka ipasavyo. (alama 2)
(h) Eleza maana mbili zinazopatikana katika sentensi:
Nenda ukaniletee mbuzi. (alama 2
(i) Tunga sentens kudhihirisha matumizi ya ngeli ya U-U. (alama 2)
(j) Andika katika usemi wa taarifa.
“Mito yetu imechafuka sana; itabidi tuungane mikono wakubwa kwa wadogo, wanaume kwa wanawake ili tuisafishe.” Mwanamazingira alituhimiza. (alama 3)
(k) Changanua sentensi ifuatayo ukitumia mistari au mishale.
Amina na Mustafa huimba taarabu. (alama 4)
(I) Eleza matumizi ya ku katika sentensi:
Sikumwelewa alivyoeleza namna ya kuwatunza mbwa wake. (alama 2)
(m) Tunga sentensi sahihi ukitumia kitenzi la katika kauli ya kutendwa. (alama 2)
(n) Eleza kazi ya kila kitenzi katika sentensi:
Mkulima angetaka kupalilia shamba lake mapema. (alama 4)
(o) Taja na utofautishe vipasuo vya ufizi. (alama 4)
(p) Onyesha jinsi moja moJa ya matumizi ya viwakifishi vifuatavyo:)
(i) Nusu koloni (;) (alama 1)
(ii) Herufi kubwa (alama 1)
(iii) Kishangao (!) (alama 1)
4. ISIMUJAMII (ALAMA 10)
“Benki yenyewe haina kitu…CD4 count yake iko chini.-Ni emergency…Tutampoteza ikikosekana.”
(a) Taja sajili inayorejelewa na maneno haya. (alama 2)
(b) Fafanua sifa nne zinazoh’usishwa na sajili hiyo. (alama 8)
KCSE Kiswahili Paper 3 2010
Find KCSE Kiswahili Paper 3 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Kiswahili Paper 3 Past paper
FASIHI SEHEMU A: USHAIRI (ALAMA 20)
1. (LAZIMA)
Soma shairi hili kisha ujibu maswali yanayofuata.
Dhamiri yangu
Dhamiri imenifunga shingoni.
Nami kama mbuzi nimefungwa Kwenye mti wa utu.
Kamba ni fupi Na nimekwishachora duara.
Majani niwezayo kufikia yote nimekula.
Ninaona majani mengi mbele yangu
Lakini siwezi kuyafikia: kamba, kamba.
Oh! Nimefungwa kama mbwa.
Nami kwa mbaya bahati, katika
Uhuru kupigania, sahani ya mbingu
Nimeipiga teke na niigusapo kwa mdomo
Mbali zaizi inakwenda na siwezi tena
Kuifikia na hapa nilipofungwa
Nimekwisha pachafua na kuhama siwezi.
Kamba isiyoonekana haikatiki.
Nami sasa sitaki ikatike, maana,
Mbuzi wa kamba alipofunguliwa, mashamba.
Aliharibu na mbwa aliuma watu.
Ninamshukuru aliyenifunga hapa
Lakini lazima nitamke kwa nguvu
“Hapa nilipo sina uhuru!”
(E. Kezilahabi)
(a) Taja mambo manne ambayo mshairi analalamikia. (alama 4)
(b) Kwa nini mshairi haoni haja ya yeye kuwa huru? (alama 2)
(c) Eleza maana ya mshororo ufuatao kama ulivyotumiwa katika shairi.
“kamba isiyoonekana haikatiki.” (alama 2)
(d) Taja na utoe mifano ya aina mbili za tamathali zilizotumika katika shairi hili. (alama 4)
(e) Kwa kutoa mifano miwili, eleza jinsi matumizi ya mishata yanavyojitokeza katika shairi hili. (alama 4)
(f) Andika ubeti wa pili,kwa lugha nathari. (alama 4)
SEHEMU B: RIWAYA
S.A. Mohammed: Utengano
2. “…wewe kwako toka lini mwanamke kuwa mtu? Wangapi umewatenda?”
(a) Eleza muktadha wadondoo hili. (alama 4)
(b) Kwa kutoa mifano minne mwafaka, dhihirisha ukweli wa dondoo hili. (alama 16)
3. Kwa kurejelea vipengele vifua tavyo vya matumizi ya lugha katika riwaya ya Utengano, onyesha jinsi mwandishi amevitumia kufanikisha maudhui:
(i) Uzungumzinafsi (alama 10)
(ii) Taswira (alama 10)
SEHEMU C: TAMTHILIA
Kithaka wa Mberia: Kifo Kisimani
4. “Dalili ya mvua ni mawingu.” Kwa kuzingatia utawala wa Mtemi Bokono, thibitisha usemi huu. (alama 20)
5. “Nitoeni! Nitoeni kaburini. Ondoeni udongo. Ondoeni udongo nitoke kaburini.”
(a) Eleza muktadha wa dondoo hiii. (alama 4)
(b) Taja na ueleze tamathali za usemi mbilii zilizotumiwa katika dondoo hili. (alama 4)
(c) Kwa kurejelea tamthiliya nzima, fafanua hoja sita kuonyesha jinsi dondoo hili linaloonyesha kinyume cha mambo. (alama 12)
SEHEMU D: HADITHI FUPI IMA FASIHI SIMULIZI
K.W. Wamitila: mayai waziri wa Maradhi na Hadithi Nyingine
6. “Ana nini mtoto huyu! Ninamtesekea na ufakiri wote huu nilionao…”
(a) Eleza muktadha wa dondoo hili. (alama 4)
(b) Eleza tatizo alilokuwa nalo anayerejelewa kisha ufafanue vitendo vinavyodhihirisha kwamba aiikuwa na tatizo. (alama 6)
(c) Anayetoa kauli hii alikuwa na msimamo gani kuhusu tatizo la mtoto? (alama 4)
(d) Kwa kutoa mifano mitatu mwafaka, eleza hali zinazoweza kulaumiwa kwa tatizo ia anayerejelewa. (alama 6)
FASIHI SIMULlZI
7. Huku ukitoa mifano mwafaka, linganisha na utofautishe kipera chsf”‘ vitendawili na kile cha methati. (alama 20)
KCSE Home Science Paper 1 2010
Find KCSE Home Science Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Home Science Paper 1 Past paper
SETION A (40 MARKS)
1. What do you understand by the term food hygiene? (1 mark)
2. Give two functions of sodium in the body? (2 marks)
3. State two disadvantages of reheating food. (2 marks)
4. Highlight two characteristics of buffet service. (2 marks)
5. Identify a nutritional disorder associated with high consumption of each of the following:
(i) Sugar, (½ mark)
(ii) Fluorine (½ mark)
6. Give two reasons why butter is suitable for creaming in cake making. (2 marks)
7. Explain the following terms:
(i) Inflation (1 mark)
(ii) Consumer rights (1 mark)
8. State two remedies for morning sickness during pregnancy. (2 marks)
9. Give two reasons why weaning a baby too early is discouraged. (2 marks)
10. Name two opportunistic diseases related to HIV and AIDS. (1 mark)
11. Give one reason for increasing iron in a lactating mother’s diet. (1 mark)
12. List two types of brushes used for removing dirt from surfaces in the home. (2 marks)
13. Define the term value in relation to colour. (1 mark)
14. Name two insects which would cause poisonous stings. (1 mark)
15. Give two surfaces in the house where a low all-round flower arrangement may be used. (1 mark)
16. Mention two physical changes in puberty that are unique to girls. (2 marks)
17.(i) List two types of bleaches and give one example in each case. (2 marks)
(ii) Give another use of laundry blue on garments apart from whitening. (1 mark)
18. Arrange the following laundry processes in the correct order. (2 marks)
Stain removal (i) ……………………………………………
Steeping (ii) ……………………………………………
Repairing (iii) ……………………………………………
Sorting (iv) ……………………………………………
19. Identify two types of “eyes” used for completing the hook fastening in garment in construction. (1 mark)
20. Mention three desirable qualities of fabrics for making P.E. shorts. (3 marks)
21. State two temporary stitches used to hold fullness before making permanent stitches. (1 mark)
22.State two characteristics of a well made dart. (2 marks)
23. Give one point to bear in mind when cutting a worked button hole. (1 mark)
24. Differentiate between a bound opening and a continuous wrap opening. (2 marks)
SECTION B ( 20 MARKS)
25. You are planning to travel with your one year old sister. Give the procedure you would use to:
(a) Clean the baby’s plastic cup you will use on the way. (4½ mark)
(b) Clean an aluminium saucepan that was previously used to boil the baby’s milk: (5 marks)
(c) Launder a coloured linen shirt with a fresh tea stain. ( 10½ marks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions in this section
26. (a) What do you understand by comparative shopping? (2 marks)
(b) Identify four functions of the Kenya Consumer Association. (4 marks)
(c) Explain three functions of fats and oils in the body. (6 marks)
(d) Explain how the following factors contribute to successful meal planning:
(i) Nutritional balance; (2 marks)
(ii) Climate; (2 marks)
(iii) Texture; (2 marks)
(iv) Individual requirements. (2 marks)
27.(a) Explain three processes to be carried out on a fabric before laying out patterns. (6 marks)
(b) Outline five processes carried out on the skirt of an apron with a bib in readiness for attachment. (5 marks)
(c) Highlight five reasons why timely repair of household articles is important. (5 marks)
(d) Draw a symbol for each of the following care instructions:
(i) handwash with temperature the hand can withstand; ( 1 mark)
(ii) hang, to dry on a clothe’s line; ( 1 mark)
(iii) Do not dry-clean; ( 1 mark)
(iv) Use a cool iron of about 120°C. ( 1 mark)
28. (a) State three advantages of lining curtains. (3 marks)
(b) Outline six precautions to take when using electrical appliances in the home. (6 marks)
(c) Identify five activities carried out in the management of amoebic dysentry. (5 marks)
(d) Highlight six points to observe when looking after a sick person. (6 marks)
KCSE History and Government Paper 2 2010
Find KCSE History and Government Paper 2 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education History and Government Paper 2 Past paper
Section A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
1. State the scientific theory that explains the origin of human beings. (1 mark)
2. State two uses of stone tools by early people during the Old Stone Age period. (2 marks)
3. Identify the method used to plant cereal crop when early agriculture began. (1 mark)
4. Name two metals that were used as currency in pre-colonial Africa. (2 marks)
5. State one advantage of using the pipeline over vehicles in transporting oil. (1 mark)
6. Give the two main items of the Trans-Saharan trade. (2 marks)
7. Identify two social functions of the ancient city of Athens in Greece. (2 marks)
8. Name the chartered company that was used to administer Tanganyika during the process of colonization. (1 mark)
9. Which was the main factor that unified the communities of the Shona Kingdom during the pre-colonial period? (1 mark)
10. State two functions of the Lukiiko in the Buganda Kingdom during the 19th Century. (2 marks)
11. Give one economic reason which made European countries to scramble for colonies in Africa. (1 mark)
12. State one way in which the Ndebele benefited after the British-Ndebele war of 1893 to 1896. (1 mark)
13. Identify two economic results of the First World War (2 marks)
14. Give two principal organs of the United Nations. (2 marks)
15. Identify two ways in which Mwalimu Julius Nyerere promoted the development of Education in Tanzania after independence. (2 marks)
16. State one condition that a country should fulfill in order to become a member of the Non-Aligned Movement. (1 mark)
17. Identify one parliamentary duty of the Monarch in Britain. (1 mark)
SECTION B (45 marks)
Answer any three questions from this section
18. (a) State five reasons why early people domesticated crops and animals during the neo-lithic period. (5 marks)
(b) Explain five causes of food shortages in Africa today. (10 marks)
19. (a) Give three problems faced by factory workers in Europe during the Industrial Revolution. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six factors that have promoted industrialization in South Africa. (12 marks)
20. (a) Give three methods used by European Powers to establish colonial rule Africa. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six results of the collaboration between the Baganda and the British during the process of colonization. (12 marks)
21. (a) State three ways used by nationalist in Ghana to fight for independence. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six factors that led to the development of African Nationalism in Ghana. (12 marks)
SECTION C (30 marks)
Answer any two questions from this section
22. (a) Give three conditions which one had to fulfill in order to become a French citizen in Senegal. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six differences between the use of British indirect rule and the French Assimilation Policy. (12 marks)
23. (a) State the role played by the United States of America in ending the Second World War. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six causes of the war after 1945. (12 marks)
24. (a) Identify three duties performed by the Secretary-General of the new east African Community established in 2001. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six benefits of the new East African Community established in 2001. (12 marks)
KCSE History and Government Paper 1 2010
Find KCSE History and Government Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education History and Government Paper 1 Past paper
Section A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
1. Give the meaning of history. (1 mark)
2. Identify one age-grade for elders among the-Akamba. (1 mark)
3. State the first settlement area of the Luo during their migration from Sudan. (1 mark)
4. Name one early Christian missionary who worked in Kenya. (1 mark)
5. State two characteristics of independent churches in Kenya during the colonial period. (2 marks)
6. Identify the constitutional change that increased the number of African members to the legislative council in Kenya in 1957. (1 mark)
7. Identify one Asian who took part in the struggle for independence in Kenya. (1 mark)
8. Name one African political party whose leaders attended the 2nd Lancaster House Conference in 1962. (1 mark)
9. Identify two Educational Commissions appointed by the government of independent Kenya to review the education system. (2 marks)
10. Give the main reason why the government of Kenya introduced the Constituency Development Fund (CDF). (1 mark)
11. State two ways in which the government has promoted the culture of the people of Kenya since independence. (2 marks)
12. Identify two conditions that one must fulfill in order to register as a voter in Kenya. (2 marks)
13. Give two special courts in Kenya. (2 marks)
14. State two duties of the leader of Government Business in parliament in Kenya. (2 marks)
15. Identify two symbols of national unity in Kenya. (2 marks)
16. Give two reasons that can make a registered person to lose citizenship in Kenya. (2 marks)
17. Give one type of human rights. (1 mark)
SECTION B (45 marks)
Answer any three questions from this section
18. (a) Give three reasons which influenced the migration of the Plains Nilotes to Kenya during the pre-colonial period. (5 marks)
(b) Explain five results of the migration and settlement of the Maasai in Kenya during the pre-colonial period. (10 marks)
19.(a) Give three reasons why the early-visitors, came to Kenyan-coast before 1500 A.D. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six factors that contributed to the development of trade between the Kenya coast and the outside world by 1900. (12 marks)
20. (a) State three socio-economic reasons why Britain colonized Kenya in the 19th Century. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six factors that contributed to the formation of political associations in Kenya before 1939. (12 marks)
21. (a) State three ways in which the government of Kenya facilitated the acquisition of land for Africans after 1963. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six challenges facing the agricultural sector in Kenya. (12 marks)
SECTION C (30 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section
22. (a) Give the structure of the provincial administration in Kenya. (5 marks)
(b) Describe five functions of the president of the Republic of Kenya. (10 marks)
23. (a) Give three reasons why the constitution is important in Kenya. (3 marks)
(b) Explain six factors that may undermine the administration of justice in Kenya. (12 marks)
24. (a) Identify five stages in the preparation of the national budget. (5 marks)
(b) Explain why it is important for the Government to prepare the national budget annually. (10 marks)
KCSE Business Studies Paper 2 2010
Find KCSE Business Studies Paper 2 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Business Studies Paper 2 Past paper
1. (a) Commodities A and B are substitutes. Using two diagrams, explain how an increase in the supply of commodity A will affect the equilibrium price and quantity demanded of commodity B.
(b) Explain five negative effects that inflation may have on the economy of a country. (10 marks)
2. (a) Describe five principles that distinguish co-operative societies from other forms of business organisations. (10 marks)
(b) Explain five ways of making face – to-face communication effective. (10 marks)
3. (a) The following balances were extracted from the books of K100 Traders for the year ended 30th June 2008.
| Item
|
Shs.
|
| Stock on 1st July 2007 | 80,200 |
| Discount received | 7,500 |
| Furniture | 3,000,000 |
| Motor vehicle | 690,000 |
| Returns inwards | 5,8000 |
| Returns outwards | 20,800 |
| Debtors | 316,800 |
| Creditors | 510,400 |
| Purchases | 1,120,000 |
| Carriage on sales | 12,700 |
| Carriage on purchases | 40,000 |
| Lighting | 15,000 |
| Sales | 1,880,000 |
| Insurance | 4,000 |
| Repairs | 230,000 |
| Water bills | 250,000 |
| General expenses | 56,700 |
| Cash | 80,000 |
| Capital | 4,000,000 |
| Bank | 520,000 |
| Bank overdraft | 2,500 |
Additional information: Stock on 30th June 2008 was valued at shs. 120,000
Prepare:
(i) Trading, Profit and Loss accounts for the year ended 30th June 2008. (9 marks)
(ii) Balance sheet as at 30th June 2008. (5 marks)
(b) Explain three factors that should be considered when choosing a means of transport. (6 marks)
4. (a) Explain five benefits that a member country may get from economic integration. (10 marks)
5. (a) Discuss five problems that a country may face when measuring her national income using the output approach. (10 marks)
(b) Explain five factors that an entrepreneur would consider when evaluating a business idea. (10 marks)
6. (a) Discuss five benefits that a customer may get by using Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) for financial transactions. (10 marks)
(b) Amina operates a fleet of Public Service Vehicles (PSVs). Explain five possible risks she can insure her business against. (10 marks)
KCSE Geography Paper 1 2010
Find KCSE Geography Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Geography Paper 1 Past paper
SECTION A
Answer ALL the Questions in this Section
1. Give three components of the solar system. (3 marks)
2.(a) Identify two types of high level clouds. . (2 marks)
(b) Draw a well labelled diagram of a hydrological cycle. . (5 marks)
3.(a) Give three causes of earthquakes. . (3 marks)
(b) Name two major earthquake zones of the world. . (3 marks)
4. (a) What is a rock? . (2 marks)
(b) Give three characteristics of sedimentary rocks. . (2 marks)
5.(a) The diagram below shows some coastal features.
Name the features marked P, Q and R. (3 marks)
(b) State two conditions necessary for the formation of a beach. (2 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
6. Study the map of Homa Bay (1 50,000) sheet 12912 provided and answer the following questions.
(a) A pipeline is to be laid from Lake Victoria along the line marked X-Y.
(i) What is the length of the piping to be used? (Give your answer to the nearest 100 metres) (2 marks)
(ii) Calculate the bearing of point Y from point X. (2 marks)
(iii) Calculate the area of the part of Lake Victoria shown on the map excluding the marshy sections. (Give your answer in square kilometres). (2 marks)
(b) The rectangle below represents the area in the map extract bounded by Eastings 54 and 60 and Northings 35 and 40. Identify and name the features marked J, K, L and M. (4 marks)
(c) (i) Explain three factors which have influenced the distribution of settlements in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
(ii) Citing evidence from the map, give two agricultural activities carried out in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
(d) Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (5 marks)
7. The map below shows some vegetation regions of the world. Use it to answer questions (a) and (b). coniferous forest
(a) (i) Name the temperate grasslands marked D, E and F. (3 marks)
(ii) Describe the characteristics of the natural vegetation found in the shaded area marked G. (6 marks)
(b) Explain how climate has influenced the existence of the following types of vegetation shown on the map.
(i) Desert vegetation; (4 marks)
(ii) Coniferous forest. (4 marks)
(c) You are required to carry out a field study of the natural vegetation within your local environment.
(i) Apart from identifying the different types of plants, state three other activities you would carry out during the field study. (3 marks)
(ii) How would you identify the different types of plants? (3 marks)
(iii) State two ways in which the information collected during the field study would be useful to the local community. (2 marks)
8(a) Describe plucking as a process in glacial erosion. (4 marks)
(b) Explain three conditions that lead to glacial deposition. (6 marks)
(c) The diagram below shows features resulting from glacial deposition on a lowland area.
(i) Name the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 marks)
(ii) Describe how terminal moraine is formed. (4 marks)
(d) Explain four positive effects of glaciation in lowland areas. (8 marks)
9(a) Differentiate between river rejuvenation and river capture. (2 marks)
(b) Give three features resulting from:
(i) river rejuvenation; (3 marks)
(ii) river capture. (3 marks)
(c) Explain the four ways through which a river transports its load. (8 marks)
(d) You are planning to carry out a field study on the lower course of a river.
(i) Give three reasons why you would require a route map. (3 marks)
(ii) State three characteristics of a river at the old stage that you are likely to observe during the field study. (3 marks)
(iii) Give three follow-up activities you would be involved in after the field study. (3 marks)
10. The diagram below represents a well developed soil profile. Use it to answer question (a).
(a) (i) Describe the characteristics of horizon B. (3 marks)
(ii) Apart from humus, name three other components of soil. (3 marks)
(iii) State three ways in which humus contributes to the quality of soil. (3 marks)
(b) (i) Differentiate between soil structure and soil texture. (2 marks)
(ii) Explain how the following factors influence the formation of soil:
<> topography; (6 marks)
<> time. (2 marks)
(c) Explain how the following farming practices may lead to loss of soil fertility:
(i) overgrazing; (2 marks)
(ii) frequent ploughing; (2 marks)
(iii) continuous irrigation. (2 marks)
KCSE English Paper 3 2010
Searching for KCSE English Past papers? Find KCSE English Paper 3 2010.
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education English Paper 3 Past paper
Dowload KCSE English Paper 3 2010 Here
KCSE English Paper 2 2010
Searching for KCSE English Past papers? Find KCSE English Paper 2 2010.
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education English Paper 2 Past paper
Download KCSE English Paper 2 2010 Here
KCSE Business Studies Paper 1 2010
Find KCSE Business Studies Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Business Studies Paper 1
1. In the spaces provided below indicate the type of utility created by each of the following commercial activities. (4 marks)
| Commercial activity | Type of utility |
| (i) Selling goods to customers; | |
| (ii) Transporting goods; | |
| (iii)Storekeeping; | |
| (iv) Making a chair |
2. Give five reasons why the government may find it necessary to start a parastatal. (5 marks)
3. Name the types of warehouses associated with each of the statements given below: (4 marks)
| Statement | Type of Warehouse |
| (i) Goods can be stored before payment of customs duty. | |
| (ii) Individuals can hire storage facilities. | |
| (iii) Goods are stored from several manufacturers. | |
| (iv) Specialised goods are stored. |
4. The figure below shows a shift in the supply curve of a given commodity.
Outline four factors that may have caused the shift in the supply curve torn S0 to S1. (4 marks)
5. The balances given below relate to Enotika Traders for the year ended 31st December 2008.
| Kshs. | |
| Capital | ? |
| 2 year bank loan | 230,020 |
| Creditors | 95,200 |
| Fixed assets | 480,000 |
| Current assets | 145,220 |
Prepare a balance sheet as at 31st December 2008. (5 marks)
6. Give two reasons why a three column cashbook is used both as journal and a ledger. (4 marks)
7. The management of national debt, credit control and lender of last resort are some of the functions of the Central Bank. Match these functions with the statements given below. (3 marks)
Statement
| Statement | Function |
| (i) Repayment of Government securities as they mature. | |
| (ii)Receipt of treasury bills to secure loans. | |
| (iii) Directing commercial banks on the preferred sectors to lend money. |
ed in international trade. (4 marks)
(i) LOCO
(ii) CIF
(iii) F.A.S
(iv) F.O.Q
9. The manager of Tasa Limited constantly walks around various departments. State four merits of this style of management. (4 marks)
10. State four reasons why the government should create an enabling environment for investors. (4 marks)
11. Outline four differences between insurance and assurance. (4 marks)
| Insurance
|
Assurance
|
| (i) | (i) |
| (ii) | (ii) |
| (iii) | (iii) |
| (IV) | (iv) |
12. State four factors that may influence the level of national income. (4 marks)
13. Outline the difference between cash and credit transactions. (4 marks)
14.The term capital employed, working capital, owner’s equity and borrowed capital are types of capital found in a business. Match each of the statements given below with the relevant type of capital. (3 marks)
| Statement
|
Type of capital
|
| (i) Resources invested into the business by the owner. | |
| (ii) Excess of current assets over current liabilities. | |
| (iii) Amount invested into the business by outsiders. |
15. Outline four ways in which government expenditure may stabilize the economy of a country. (4 marks)
16. State four problems associated with development planning. (4 marks)
17. State four services that a wholesaler may offer to a manufacturer. (4 marks)
18. State four reasons why flower exporters would transport their produce by air rather than by sea. (4 marks)
19. The diagram below represents the relationship between population and income per capital. (4 marks)
State what is represented by P and S axes, and letters R and Q. (4 marks)
(ii) S (axis) _________________.
(iii) R _________________.
(iv) Q _________________.
20. The following information was extracted from the books of Helen Traders;
| 1/1/2008
Shs |
31/12/2008
Shs |
|
| (i) Salaries pre pre-paid | 24,800 | 52,400 |
| (ii) Salaries paid | – | 48,200 |
Prepare a salary expense account using the above information. (5 marks)
21. State four circumstances under which one may decide to start a personal business. (4 marks)
22. Highlight four ways in which a business idea can be implemented. (4 marks)
23. Outline five measures that a manager can take to improve the working environment in the office. (5 marks)
24. Highlight four challenges that a person may encounter when using a cellphone (mobile phone). (4 marks)
KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010
Searching for KCSE Computer Studies Past papers? Find KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Computer Studies Paper 1 Past paper
KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided
1. List four activities carried out by a data processing system. (2 marks)
2. (a) Define data communication. (1 mark)
(b) State two characteristics of an effective data communication system. (2 marks)
3. Explain why an intranet is a more secure way to share files within an organization. (2 marks)
4. Distinguish between a formula and a function as used in spreadsheets. (2 marks)
5. State four functions which are specific to Network Operating Systems. (4 marks)
6. The word race is appearing several times in a long story document composed using a DTP package. How would this word be safely replaced with the word content? (3 marks)
7. Study the pseudocode below and determine its output. (3 marks)
1. (a) T = 0
(b) M = 0
(c) K = 1
2. (a) M = M + T
(b) T = T + 5
(c) K = K + 1
3. Repeat step 2 while K < 3
4. Write M, T
5. Exit
8. Give two reasons why the use of finger prints and voice input can be used as reliable forms of security in computer systems. (2 marks)
9. State the purpose of each of the following memories in a computer system.
(a) RAM (1 mark)
(b) Hard disk (1 mark)
10. Explain why telecommuting is not suitable for a doctor when carrying out an operation on a patient. (2 marks)
11. Copyright laws are laws granting authors the exclusive privilege to produce, distribute, perform or display their creative works. It is a legal framework for protecting the works such as book publishing, motion-picture production and recording. State two challenges that are posed to these laws by ICT. (2 marks)
12. State two reasons why it is necessary to use standard furniture in a computer laboratory. (2 marks)
13. Explain the following terms as used in computer.
(a) Main document (1 mark)
(b) Data source (1 mark)
14. State three ways in which ICT can be used in shipping control. (3 marks)
15. A firm operates an order system that coordinates orders, raw materials and inventory across its three factories. Currently the orders are processed manually at each factory and communicated to the others over the phone. The management intends to computerise their operations. State the first two computer professionals who will be required and their roles. (4 marks)
16. (a) Machine language programs are more difficult to write than high – level language programs. State two reasons for this. (2 marks)
(b) In order to process examination results of students in a school, their names, index numbers and scores in 11 subjects are required. The average score for each student is then determined and a grade assigned. This process is repeated for all 40 students in a class.
Draw a flowchart to:
v Read a student’s name, index number and the scores in all the subjects.
v Determine the student’s average score.
v Assign a grade to the student depending on the average score as follows:
| Score | Grade |
| 80 ≤ score | A |
| 60 ≤ score < 80 | B |
| 40 ≤ score < 60 | C |
| Score < 40 | F |
v Display the student’s name, index number, average score and the grade.
v Repeat the above steps for all the students in the class. (10 marks)
(c) Below is a list of program segments in different generations of programming languages. Identify the language for each.
(i) LDA 105
SUB 40
ADD 20
(1 mark)
(ii) 10000110 10111101
0111100 0001100
(1 mark)
(iii) For x:= 1 to 10 do
write (x);
(1 mark)
17.(a) The following are some of the phases in the systems development life cycles (SDLC): system analysis, system design, system implementation, system review and maintenance. State four activities that are carried out during the system implementation phase. (4 marks)
(b) Give three reasons why system maintenance phase is necessary in SDLC. (3 marks)
(c) State two instances where observation is not a viable method of gathering information during system analysis stage. (2 marks)
(d) Various considerations should be made during input design and output design. State two considerations for each case. (4 marks)
(e) State two reasons why an organisation may use other strategies of software acquisition other than developing their own. (2 marks)
18. (a) Using two examples, explain the term field properties as used in database design. (2 marks)
(b) Below is an extract from a hospital database table.
| Patient No
|
Name
|
Date Registered
|
Amount paid
|
Remarks
|
| LDK/001 | Mathew Olang | 04/05/08 | 2500.00 | To go for x – ray |
| LDK/004 | Joy Chelimo | 07/06/08 | 1200.00 | Medicine to be ordered |
| LDK/008 | John Kamau | 09/08/08 | 3500.00 | To be admitted for further check up. |
| LDK/002 | Gerald Wasike | 02/04/05 | 800.00 | To come back for review |
(i) State with reasons the most suitable data types for the following fields: (8 marks)
I. patient No;
II. date registered;
III. amount paid;
IV. remarks;
(ii) Which would be the most appropriate primary key field for the above table? (1 mark)
(iii) What is the purpose of a primary key field in database design? (1 mark)
(iv) Describe how information about patients who registered after 09/08/06 can be extracted from the database. (3 marks)
19.(a) Explain how data in a computer system is secured using: (4 marks)
(i) Password;
(ii) User access level
(b) State three characteristics of a suitable password. (3 marks)
(c) State two characteristics of a computer that is infected by computer viruses. (2 marks)
(d) (i) The figure below shows how data is transmitted through a public telephone line.
Name A, B, C and D.
(d) (ii) State two advantages of using fibre optic cables over satellite in data communication. (2 marks)
20.(a) Using one’s complement, convert the decimal number -9 into 6-bit binary number. (3 marks)
(b) (i) State three standard coding schemes used in data representation. (3 marks)
(ii) In a certain coding scheme, each character occupies 7 bits. Letters of the alphabet are assigned consecutive codes. If letter N is represented by 1010010. What is the representation of letter A in this coding scheme? (3 marks)
(iii) Using twos complement, show how the arithmetic below would be carried out on a 8-bit computer system. (6 marks)
KCSE Christian Religious Education Paper 1 2010
Find KCSE Christian Religious Education Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Christian Religious Education Paper 1 Past paper
1.(a) Identify eight historical books in the Old Testament. (8 marks)
(b) Give seven reasons why the Bible is referred to as a library. (7 marks)
(c) State five different occasions when Christians use the Bible. (5 marks)
2.(a) State four ways in which God demonstrated His concern for the Israelites during the Exodus. (8 marks)
(b) How did the Israelites worship God when they were in the wilderness? (5 marks)
(c) Identify seven challenges that Christians face while practicing their faith in Kenya today. (7 marks)
3. (a) From the story of Naboth’s vineyard, explain the commandments which King Ahab and Queen Jezebel broke. (8 marks)
(b) With reference to 1st Kings 21: 17 – 29, give the forms of punishment prophesied by Elijah to King Ahab and Queen Jezebel. (6 marks)
(c) Why is killing condemned in traditional African communities? (6 marks)
4. (a) Outline six characteristics of true prophets in the Old Testament. (6 marks)
(b) State four ways in which the rich oppressed the poor during the time of Prophet Amos. (8 marks)
(c) Give six reasons why Christians find it difficult to help the needy in society today. (6 marks)
5. (a) Give six reasons why Jeremiah was not willing to accept the call of God to become a prophet. (6 marks)
(b) Explain four evils condemned by Prophet Jeremiah during the Temple sermon. (8 marks)
(c) State six ways in which church leaders communicate God’s message to people in Kenya today. (6 marks)
6. (a) Name six places in which sacrifices are carried out in traditional African communities. (6 marks)
(b) Give seven reasons why sacrifices are made in traditional African communities. (7 marks)
(c) State seven roles of ancestors in traditional African communities. (7 marks)
KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2010
KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2010
1. Give two disadvantages of intensive system of farming. (1 mark)
2. List four methods of farming. (2 marks)
3(a) Give the meaning of the following terms:
(i) Nitrogen fixation into the soil. (1 mark)
(ii) Phosphorus fixation in loss of soil fertility. (1 mark)
4. Give four reasons for keeping livestock health records on the farm. (2 marks)
5. Explain the relationship between scarcity and choice as used in agricultural economics. (2 marks)
6. State two reasons for land fragmentation in Kenya. (2 marks)
7. Give four advantages of individual owner operator tenure system as practiced in Kenya. (2 marks)
8. State four features that should be considered when choosing water pipes for use on the farm. (2 marks)
9. Give four reasons for treating water for use on the farm. (2 marks)
10. Name four statutory boards that are involved in the marketing of crop produce in Kenya. (2 marks)
11. State four marketing functions of Kenya Co-operative Creameries (K.C.C) (2 marks)
12. Give two reasons for carrying out each of the following operations in land preparation:
(a) Rolling; (1 mark)
(b) Leveling; (1 mark)
13. Name three recommended practices that should be carried out when clearing the bush during land preparation. (1 1/2 marks)
14. State five advantages of zero grazing (21/2 marks)
15. Give four factors that would determine the stage at which a crop is harvested. (2 marks)
16. Name two classes of weeds on the basis of each of the following:
(a) Growth cycle (1 mark)
(b) Plant morphology (1 mark)
17. Below is a diagram of a weed. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
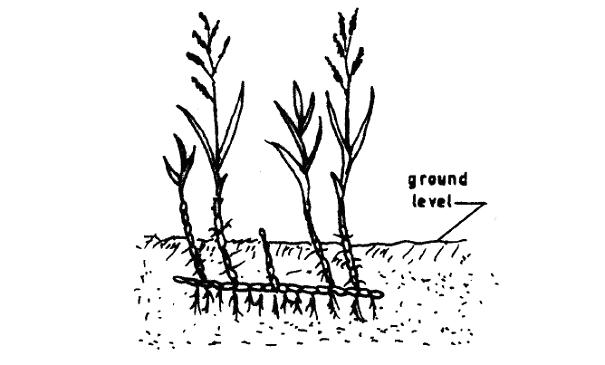
(a) Identify the weed illustrated above. (½ mark)
(b) Why is the weed illustrated above difficult to control? (1 mark)
(c) State four ways in which the weed can be controlled in a field of maize. (2 marks)
18. The table below shows pH values of different soil samples. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
| Soil Sample | pH value |
| S1 | 3 |
| S2 | 4 |
| S3 | 5 |
| S4 | 6 |
| S5 | 7 |
| S6 | 8 |
| S7 | 9 |
| S8 | 10 |
(a) Which soil sample has the highest acidity? (1 mark)
(b) State two ways in which the pH value of sample S, can be lowered. (1 mark)
(c) Which of the above soil samples is suitable for growing tea?. (½ mark)
19. Explain how agroforestry tree seeds should be prepared after collection in readiness for planting. (4 marks)
20 (a)(i) The diagrams below represent two ways in which a crop was pruned. Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
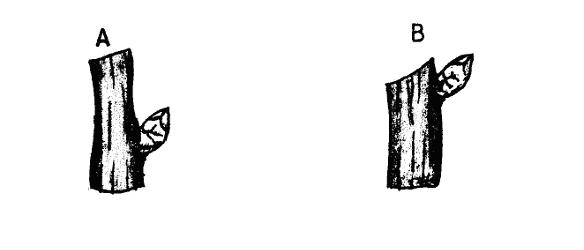
20(a)(i) Which diagram represents the correct way of pruning? (1 mark)
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (i) above. ( 1 mark )
(b) State two ways in which pruning assists in controlling crop diseases. (1 mark)
21. On 1st January 2009, Kaburu Farm started farm operations with Ksh 30,000 cash. During the month, the farm made the following transactions. Study the transactions and prepare a cash analysis for Kaburu Farm for the month of January. (5½marks)
| Date | Transaction | Amount (Kshs.) |
| 05/01/09 | Livestock sales | 80,000 |
| 08/01/09 | Crop sales | 50,000 |
| 15/01/09 | Bought seed for planting | 7,500 |
| 20/01/09 | Paid K.F.A. for fertilizer | 16,400 |
| 25/01/09 | Bought livestock feeds | 50,000 |
| 30/01/09 | Paid wages for planting & weeding | 56,000 |
| 31/01/09 | Received cash from K .C .C. for milk delivery | 120,000 |
| 31/01/09 | Paid transport charges for milk delivery | 9,000 |
Q22 (a) What do the figures 18:46:10 on a fertilizer bag represent? ( 1½ marks)
(b) Calculate the quantity of filler materials in the fertilizer in (a) above. (l mark)
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided after question 25.
Q23 (a) Explain eight factors that can encourage soil erosion. (8 marks)
(b) Describe the seven management practices that should be carried out on a vegetable nursery after sowing seeds until the seedlings are ready for transplanting. (7 marks)
(c) State five soil factors that should be considered when selecting a crop to grow in an area. (5 marks)
24(a) Outline five ways in which high temperature affects agricultural production in Kenya. (5 marks)
(b)(i) Explain four precautions that should be observed when harvesting cotton. (4 marks)
(ii) Describe the harvesting of sugar cane. (3 marks)
(c) Explain eight factors that should be considered when planning to set up a farm business. (8 marks)
25(a) Explain six physical methods that can be used to control crop pests on the farm. (6 marks)
(b) Describe the production of bulb onions under the following sub-headings:
(i) field management; (4 marks)
(ii) harvesting (3 marks)
(c) Explain seven factors that influence seed rates in crop production. (7 marks)
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2010
Find KCSE Biology Paper 3 2010 below. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Biology Past Paper – Paper 3
1. You are provided with a visking tubing, a solution labeled L, Iodine solution labeled solution E, Benedict’s solution labeled solution F and a piece of thread.
Tie one end of the visking tubing tightly using the thread provided. With the help of a syringe, put 10ml of the solution labeled L into the visking tubing. Tie the other end of the visking tubing tightly.
Ensure that there is no leakage at both ends of the visking tubing.
Wash the outside of the visking tubing with water. Place the visking tubing upright in a 100ml beaker. Add distilled water into the beaker to reach the level of the liquid in the visking tubing. Allow the set up to stand for 30 minutes or more.
(a) Using 2ml in a test – tube in each case, test for the food substance in the liquid outside the visking tubing using: (3 marks)
| TEST | Procedure
|
Observations | Conclusion |
| (i) Iodine solution (Solution E) | |||
| (ii) Benedict’s solution (solution F) |
(b) Using 2ml in a test-tube in each case, test for the food substance in the contents of the visking tubing using: (3 marks)
| TEST | Procedure
|
Observations | Conclusion |
| (i) iodine solution (Solution E) | |||
| (ii) Benedict’s solution (solution F) |
(c) Account for your results in (a) and (b) above. (3 marks)
2. The photographs labeled J, K, M1 and M2 are sections of a mammalian heart. Examine them.
(a) The blue, green and cream strings go through various blood vessels and end up at various chambers of the heart. For each string, name the chamber where the string ends and the blood vessel through which the string goes. (8 marks)
| String | Chamber | Blood vessel |
| Blue | …………………………… | …………………………… |
| Green | …………………………… | …………………………… |
| Cream 1 | . …………………………… | …………………………… |
| Cream 2 | …………………………… | …………………………… |
(b)Name the part labeled 3 in photograph K (1 mark)
(c) The parts labeled 4 and 5 are walls of two chambers of the heart. Account for the difference in the thickness of the walls. (1 marks)
(d) Photograph M1 shows two blood vessels labeled X and Y while M2 shows transverse sections of the same blood vessels. With a reason, identify the type of each of the blood vessels. (4 marks)
(e) In photograph K, indicate by letter B the part of the heart which would be cut to expose the bicuspid valve. (1 mark)
3. The photographs labeled Q, R, S and T are sections of some parts of plants.
(a) Name the type of placentation in the specimens shown in photographs Q, R and S. (3 marks)
(b) Label a seed in photographs R and S. (2 marks)
(c) Name the parts labeled 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 in photograph T (5 marks)
(d) Giving a reason in each case, name the mode of dispersal of each of the specimens in photographs Q and T. (4 marks)
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2010
Find KCSE Biology Paper 2 2010 below. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Biology – Paper 2
1. In an experiment, disinfected soaked bean seeds were put in a vacuum flask which was then fitted with a thermometer as shown in the diagram below.
The temperature readings were taken every morning for three consecutive days.
(a) Which process was being investigated? (1 mark)
(b) (i) What were the expected results? (1 mark)
(ii)Account for the answer in (b) (i) above. (2 marks)
(c) Why were the seeds disinfected? (2 marks)
(d) Why was a vacuum flask used in the set-up? (1 mark)
(e) How would a control for this experiment be set? (1 mark)
2. The diagram below shows blood circulation in a mammalian tissue.
(a) Name the parts labeled P and Q. (2 marks)
(b) Name the substances that are:
(i) Required for respiration that move out of capillaries. (1 mark)
(ii)Removed from tissue cells as a result of respiration. (1 mark)
(c) Explain how substances move from blood capillaries into the tissue cells. (3 marks)
(d) Name one component of the blood that is not found in the part labeled P. (1 mark)
3. The diagram below represents a food web in a certain ecosystem.
(a) Name the trophic level occupied by each of the following:
(i) Caterpillars (1 mark)
(ii)Small insects (1 mark)
(b) From the food web, construct two food chains which end with lizards as a tertiary consumer. (2 marks)
(c) (i) Which organisms have the least biomass in this ecosystem? (1 mark)
(ii)Explain the answer in (c) (i) above. (3 mark)
4. The diagram below shows how the iris and pupil of a human eye appear under different conditions.
(a) Name the structures labeled X and Y. (1 mark)
(b) (i) State the condition that leads to the change in appearance shown in the diagram labeled B. (1 mark)
(ii) Describe the changes that lead to the appearance of the iris and pupil as shown in the diagram labeled B. (4 marks)
(iii) What is the significance of the changes described in (b) (ii) above. (1 mark)
5. When pure breeding black guinea pigs were crossed with pure breeding white guinea pigs, the offspring had a coat with black and white parches.
(a) Using letter G to represent the gene for black coat colour and letter H for white coat colour, work out the genotypic ratio of F2. (5 marks)
(b) State the phenotypic ratio of Fs. (1 mark)
(c) (i) Name the term used when two alleles In heterozygous state are fully expressed phenotypically in an organism. (1 mark)
(ii) Give an example of a trait in human beings where the condition whose term is named in (c) (i) above expresses itself. (1 mark)
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
6. In an experiment to investigate a certain physiological process, a boiling tube labeled A and a test tube labeled B were covered with cotton wool. The two tubes were
simultaneously filled with hot water and fitted with thermometers. The experimental set- up was as in the diagrams below.
Temperature readings were taken at the start and after every two minutes for twenty minutes. The results were as shown in the table below.
| Time (Minutes) | Temperature (°c)
|
|
| Boiling tube A
|
Test tube B
|
|
| 0 | 60 | 60 |
| 2 | 59 | 54 |
| 4 | 57 | 50 |
| 6 | 55 | 46 |
| 8 | 53 | 43 |
| 10 | 52 | 40 |
| 12 | 51 | 37 |
| 14 | 49 | 35 |
| 16 | 48 | 33 |
| 18 | 47 | 32 |
| 20 | 46 | 30 |
(a) Using the same axes, draw graphs of temperature against time. (6 marks)
(b) (i) Work out the rate of heat loss in the boiling tube labeled A and test-tube labeled B between the 5th and 15th minutes. (2 marks)
(ii) Account for the answers in (b) (i) above. (2 marks)
(iii) How does the explanation in (b) (ii) above apply to an elephant and a rat? (2 marks)
(c) (i) State the role of the cotton wool in this experiment. (1 mark)
(ii) Name two structures in mammals that play the role stated in (c) (i) above. (2 marks)
(d) State three advantages of having constant body temperature in mammals. (3 marks)
7. Describe the process of fertilization in flowering plants. (20 marks)
8. Describe how a finned fish such as Tilapia moves in water. (20 marks)
KCSE Chemistry Paper 3 2010
for KCSE Chemistry Past papers? Find KCSE Chemistry Paper 3 2010.
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 3 Past paper
Download KCSE Chemistry Paper 3 2010 HereKCSE Chemistry Paper 3 2010 Here
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2010
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2010 below
1. State the name given to the study of:
(a) The cell (1 mark)
(b) Microorganisms (1 mark)
2. The diagram below shows a transverse section of a plant organ.
(a) Name the plant organ from which the section was obtained. (1 mark)
(b) (i) Name the class to which the plant organ was obtained. (1 mark)
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above. (1 mark)
(c) Name the part labelled X. (1 mark)
3. State the functions of:
(a) Ribosomes. (1 mark)
(b) Lysosomes. (1 mark)
4. The diagram below shows a specialized plant cell.
(a) (i) Name the cell. (1 mark)
(ii) Name the parts labeled D and E. (2 marks)
(b) State the function of the part labeled C. (1 mark)
5. State three ways in which a respiratory surface is adapted to its function. (3 marks)
6. State one function for each of the following:
(a) Cerebellum (1 mark)
(b) Medulla oblongata (1 mark)
7. Distinguish between haemolysis and plasmolysis. (2 marks)
8. State three external differences between chilopoda and diplopoda. (3 marks)
9. State two ways in which chloroplasts are adapted to their function. (2 marks)
10. State two advantages of hybrid vigour. (2 marks)
11. The diagram below shows a transverse section of a leaf.
(a) Name the habitat of the plant from which the leaf was obtained. (1 marks)
(b) Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above. (2 marks)
12. The diagram below illustrates the structure of bread mould.
(a) Name the part labeled J. (1 marks)
(b) State the functions of the structure labeled K. (2 marks)
13. What is meant by the following terms?
(a) Habitat (1 marks)
(b) Ecosystem (1 marks)
14. Explain why it is not advisable to be in poorly ventilated room with a burning charcoal stove. (3 marks)
15. A potted plant was kept in the dark for 48 hours. Two leaves X and Y were treated as shown in the diagram below.
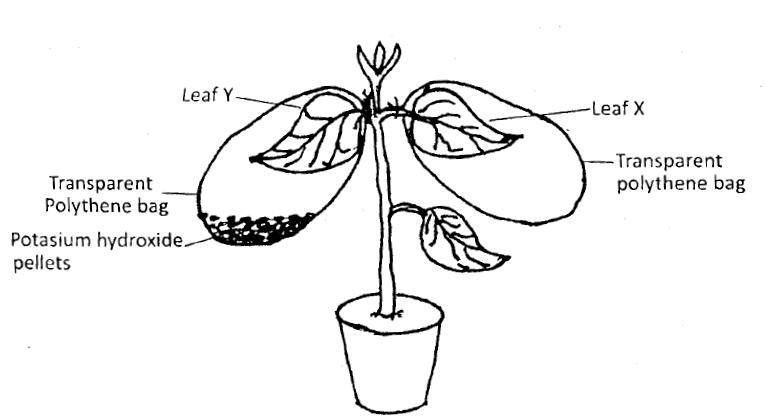
The experimental set-up was kept in sunlight for 6 hours after which a starch test was carried out on the two leaves.
(a) What were the results of the starch test on leaves X and Y? (2 marks)
(b) Give reasons for your answers in (a) above. (2 marks)
16. What is the role of bile salts in digestion in humans? (2 marks)
17. The following is the dental formula of a certain mammal:
(a) State the likely mode of feeding for the mammal. (1 mark)
(b) Give a reason for your answer in (a) above. (1 mark)
18. Give two reasons why animals have specialized organs for excretion as compared to plants. (2 marks)
19. State the changes that occur in arterioles in the human skin during thermoregulation. (2 marks)
20. State two advantages of internal fertilization in humans. (2 marks)
21. The diagram below represents part of the human skeleton.
(a) Name the part labeled P. (1 mark)
(b) (i) Name the bone that articulates with the part labeled Q. (1 mark)
(ii) What type of joint is formed between the part labeled Q and the bone named in (b)(i) above? (1 mark)
22. What is the function of the following structures in the human reproductive organs?
(a) Fallopian tubes. (1 mark)
(b) Epididymis (1 mark)
(c) Scrotal sac (1 mark)
23. Explain three ways in which red blood cells are adapted to their function. (3 marks)
24. (a) State two ideas proposed by Lamark in his theory of evolution. (2 marks)
(b) Why is Lamark’s theory not acceptable. (1 mark)
25. State three factors that contribute to the deceleration phase in the population curve of an organism. (3 marks)
26. State one survival value for each of the following in plants:
(a) Thigmotropism in stems (1 mark)
(b) Geotropism in roots (1 mark)
27. (a) What is meant by the term non-disjunction?
(b) Give an example of a genetic.disorder caused by:
(i) Non-disjunction. (1 mark)
(ii)Gene mutation. (1 mark)
28. State three structural differences between arteries and veins. (3 marks)
29. The diagram below represents a female cone.
(a) Name the subdivision of the plant from which the cone was obtained. (1 mark)
(b) Other than the presence of cones, name two other external features that identify plants in the subdivision named in (a) above. ? (2 marks)
30. What is meant by the term apical dominance? (3 marks)
KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010
Searching for KCSE Computer Studies Past papers? Find KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Computer Studies Paper 1 Past paper
KCSE Computer Studies Paper 1 2010
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided
1. List four activities carried out by a data processing system. (2 marks)
2. (a) Define data communication. (1 mark)
(b) State two characteristics of an effective data communication system. (2 marks)
3. Explain why an intranet is a more secure way to share files within an organization. (2 marks)
4. Distinguish between a formula and a function as used in spreadsheets. (2 marks)
5. State four functions which are specific to Network Operating Systems. (4 marks)
6. The word race is appearing several times in a long story document composed using a DTP package. How would this word be safely replaced with the word content? (3 marks)
7. Study the pseudocode below and determine its output. (3 marks)
1. (a) T = 0
(b) M = 0
(c) K = 1
2. (a) M = M + T
(b) T = T + 5
(c) K = K + 1
3. Repeat step 2 while K < 3
4. Write M, T
5. Exit
8. Give two reasons why the use of finger prints and voice input can be used as reliable forms of security in computer systems. (2 marks)
9. State the purpose of each of the following memories in a computer system.
(a) RAM (1 mark)
(b) Hard disk (1 mark)
10. Explain why telecommuting is not suitable for a doctor when carrying out an operation on a patient. (2 marks)
11. Copyright laws are laws granting authors the exclusive privilege to produce, distribute, perform or display their creative works. It is a legal framework for protecting the works such as book publishing, motion-picture production and recording. State two challenges that are posed to these laws by ICT. (2 marks)
12. State two reasons why it is necessary to use standard furniture in a computer laboratory. (2 marks)
13. Explain the following terms as used in computer.
(a) Main document (1 mark)
(b) Data source (1 mark)
14. State three ways in which ICT can be used in shipping control. (3 marks)
15. A firm operates an order system that coordinates orders, raw materials and inventory across its three factories. Currently the orders are processed manually at each factory and communicated to the others over the phone. The management intends to computerise their operations. State the first two computer professionals who will be required and their roles. (4 marks)
16. (a) Machine language programs are more difficult to write than high – level language programs. State two reasons for this. (2 marks)
(b) In order to process examination results of students in a school, their names, index numbers and scores in 11 subjects are required. The average score for each student is then determined and a grade assigned. This process is repeated for all 40 students in a class.
Draw a flowchart to:
v Read a student’s name, index number and the scores in all the subjects.
v Determine the student’s average score.
v Assign a grade to the student depending on the average score as follows:
| Score | Grade |
| 80 ≤ score | A |
| 60 ≤ score < 80 | B |
| 40 ≤ score < 60 | C |
| Score < 40 | F |
v Display the student’s name, index number, average score and the grade.
v Repeat the above steps for all the students in the class. (10 marks)
(c) Below is a list of program segments in different generations of programming languages. Identify the language for each.
(i) LDA 105
SUB 40
ADD 20
(1 mark)
(ii) 10000110 10111101
0111100 0001100
(1 mark)
(iii) For x:= 1 to 10 do
write (x);
(1 mark)
17.(a) The following are some of the phases in the systems development life cycles (SDLC): system analysis, system design, system implementation, system review and maintenance. State four activities that are carried out during the system implementation phase. (4 marks)
(b) Give three reasons why system maintenance phase is necessary in SDLC. (3 marks)
(c) State two instances where observation is not a viable method of gathering information during system analysis stage. (2 marks)
(d) Various considerations should be made during input design and output design. State two considerations for each case. (4 marks)
(e) State two reasons why an organisation may use other strategies of software acquisition other than developing their own. (2 marks)
18. (a) Using two examples, explain the term field properties as used in database design. (2 marks)
(b) Below is an extract from a hospital database table.
| Patient No
|
Name
|
Date Registered
|
Amount paid
|
Remarks
|
| LDK/001 | Mathew Olang | 04/05/08 | 2500.00 | To go for x – ray |
| LDK/004 | Joy Chelimo | 07/06/08 | 1200.00 | Medicine to be ordered |
| LDK/008 | John Kamau | 09/08/08 | 3500.00 | To be admitted for further check up. |
| LDK/002 | Gerald Wasike | 02/04/05 | 800.00 | To come back for review |
(i) State with reasons the most suitable data types for the following fields: (8 marks)
I. patient No;
II. date registered;
III. amount paid;
IV. remarks;
(ii) Which would be the most appropriate primary key field for the above table? (1 mark)
(iii) What is the purpose of a primary key field in database design? (1 mark)
(iv) Describe how information about patients who registered after 09/08/06 can be extracted from the database. (3 marks)
19.(a) Explain how data in a computer system is secured using: (4 marks)
(i) Password;
(ii) User access level
(b) State three characteristics of a suitable password. (3 marks)
(c) State two characteristics of a computer that is infected by computer viruses. (2 marks)
(d) (i) The figure below shows how data is transmitted through a public telephone line.
Name A, B, C and D.
(d) (ii) State two advantages of using fibre optic cables over satellite in data communication. (2 marks)
20.(a) Using one’s complement, convert the decimal number -9 into 6-bit binary number. (3 marks)
(b) (i) State three standard coding schemes used in data representation. (3 marks)
(ii) In a certain coding scheme, each character occupies 7 bits. Letters of the alphabet are assigned consecutive codes. If letter N is represented by 1010010. What is the representation of letter A in this coding scheme? (3 marks)
(iii) Using twos complement, show how the arithmetic below would be carried out on a 8-bit computer system. (6 marks)
KCSE English Paper 1 2010
Searching for KCSE English Past papers? Find KCSE English Paper 1 2010.
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education English Paper 1 Past paper
Download English KCSE English Paper 1 2010 Here
KCSE Mathematics Paper 1 2010
Find KCSE Mathematics Paper 1 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Mathematics Paper 1 Past paper
SECTION A (50 MARKS)
1. Without using a calculator evaluate:
![]()
(3 marks)
2. Kutu withdrew some money from a bank. He spent 3/8 of the money to pay for Mutua’s school fees and 2/5 to pay for Tatu’s school fees. If he remained with Ksh 12 330, calculate the amount of money he paid for Tatu’s school fees. (4 marks)
3. A straight line L passes through the point (3, -2) and Is perpendicular to a line whose equation is 2y – 4x = 1.
Find the equation of L in the form y = mx + c, where m and c are constants. (3 marks)
4. A bus left a petrol station at 9.20a.m. and traveled at an average speed of 75km/h to a town N. At 9.40 a.m. a taxi. traveling at an average speed of 95km/h, left the same petrol station and followed the route of the bus. Determine the distance, from the petrol station, covered by the taxi at the time it caught up with the bus. (3 marks)
5. The sum of three consecutive odd integers is greater than 219. Determine the the first three such integers. (3 marks)
6. A Kenyan company received US Dollars 100 000. The money was converted into Kenya shillings in a bank which buys and sells foreign currencies as follows:
| Buying
(in Kenya shillings) |
Selling
(in Kenya shillings) |
|
| 1 US Dollar | 77.24 | 77.44 |
| 1 Sterling Pound | 121.93 | 122.27 |
(a) Calculate the amount of money, in Kenya shillings, the company received. (2 marks)
(b) The company exchanged the Kenya shillings calculated in (a) above, into sterling pounds to buy a car from Britain. Calculate the cost of the car to the nearest sterling pound. (2 marks)
7. In the figure below, OPQR is a trapezium in which PQ is parallel to OR and M is the mid-point of QR. OP = p, OR = r and PQ = 1/3OR.
Find OM in terms of p and r (3 marks)
8. Without using mathematical tables or a calculator, evaluate
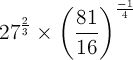 (3 marks)
(3 marks)
9. The figure below is a net of a cube with some dots on two faces
Given that the number of dots on pairs of opposite faces add up to 7, fill in appropriate dots in each of the empty faces. (2 marks)
10. Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only, construct a rhombus QRST in which angle TQR=60°and QS=10cm. (3 marks)
11. A fruit vendor bought 1948 oranges on a Thursday and sold 750 of them on the same day. On Friday, he sold 240 more oranges than on Thursday. On Saturday he bought 560 more oranges. Later that day, he sold all the oranges he had at a price of Ksh 8 each. Calculate the amount of money the vendor obtained from the sales of Saturday. (4 marks)
12. Simplify the expression:
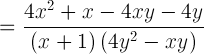
(3 marks)
13. Given that 3Ɵ = Cos 2Ɵ° find the value of Ɵ.
14. A cylindrical solid whose radius and height are equal has a surface area of 154cm2. Calculate its diameter, correct to 2 decimal places. (Take pi = 3.142) (3 marks)
15. The figure below shows two sectors in which CD and EF are arcs of concentric circles, centre 0. Angle COD = 2/3 radians and CE = DF = 5cm.
If the perimeter of the shape CDFE is 24cm, calculate the length of OC. (3 marks)
16. The histogram shown represents the distribution of heights of seedlings of a certain plant.
The shaded area in the histogram represents 20 seedlings. Calculate the percentage number of seedlings with heights of at least 23cm but less than 27cm. (3 marks)
17. A saleswoman is paid a commission of 2% on goods sold worth over Ksh 100 000. She is also paid a monthly salary of Ksh 12 000. In a certain month, she sold 360 handbags at Ksh 500 each.
(a) Calculate the saleswoman’s earnings that month. (3 marks)
(b) The following month, the saleswoman’s monthly salary was increased by 10%. Her total earnings that month were Ksh 17 600.
Calculate:
(i) the total amount of money received from the sales of handbags that month; (5 marks)
(ii) the number of handbags sold that month. (2 marks)
18. A carpenter constructed a closed wooden box with internal measurements 1.5 metres long, 0.8 metres wide and 0.4 metres high. The wood used in constructing the box was 1.0 cm thick and had a density of 0.6g/cm3.
(a) Determine the:
(i) volume, in cm3, of the wood used in constructing the box; (4 marks)
(ii) mass of the box, in kilograms, correct to 1 decimal place. (2 marks)
(b) Identical cylindrical tins of diameter 10cm, height 20cm with a mass of 120g each were packed in the box.
Calculate the:
(i) maximum number of tins that were packed; (2 marks)
(ii) total mass of the box with the tins. (2 marks)
19. (a) Find A-1, the inverse of matrix:
![]()
(2 marks)
(b) Okello bought 5 Physics books and 6 Mathematics books for a total of Ksh 2,440. Ali bought 7 Physics books and 9 Mathematics books for a total of Ksh 3,560.
(i) Form a matrix equation to represent the above information. (1 mark)
(ii) Use matrix method to find the price of a Physics book and that of a Mathematics book. (3 marks)
(c) A school bought 36 Physics books and 50 Mathematics books. A discount of 5% was allowed on each Physics book whereas a discount of 8% was allowed on each Mathematics book. Calculate the percentage discount on the cost of all the books bought. (4 marks)
20. The boundaries PQ, QR, RS and SP of a ranch are straight lines such that: Q is 16km on a bearing of 040° from P, R is directly south of Q and east of P and S is 12km on a bearing of 120° from R.
(a) Using a scale of 1cm to represent 2km, show the above information in a scale drawing. (3 marks)
(b) From the scale drawing determine:
(i) the distance, in kilometers, of P from S (2 marks)
(ii) the bearing bf P from S (2 marks)
(d) Calculate the area of the ranch PQRS in square kilometres. (3 marks)
21. Motorbike A travels at 10km/h faster than motorbike B whose speed is x km/h. Motorbike A takes 11/2 hours less than motorbike B to cover a 180 km journey.
(a) Write an expression in terms of x for the time taken to cover the 180km Journey by:
(i) motorbike A (1 mark)
(ii) motorbike B (1 mark)
(b) Use the expression in (a) above to determine the speed, in km/h of motorbike A. (6 marks)
(c) For a journey of 48km, motorbike B starts 10 minutes ahead of motorbike A. Calculate, in minutes, the difference in the time of their arrival at the destination. (2 marks)
22. In the figure below, ABCD is a square. Points P, Q, R and S are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively.
(a) Describe fully:
(i) a reflection that maps triangle QCE onto triangle SDE; (1 mark)
(ii) an enlargement that maps triangle QCE onto triangle SAE; (2 marks)
(iii) a rotation that maps triangle QCE onto triangle SED. (3 marks)
(b) The triangle ERC is reflected on the line BD. The image of ERC under the reflection is rotated clockwise through an angle of 90° about P. Determine the images of R and C:
(i) under the reflection; (2 marks)
(ii) after the two successive transformations. (2 marks)
23. The frequency distribution table below represents the number of kilograms of meat sold in a butchery.
(a) State the modal frequency. (1 mark)
(b) Calculate the mean mass. (5 marks)
(c) Calculate the median mass. ( 4 marks)
24. A rectangular box open at the top has a square base. The internal side of the base is x cm long and the total internal surface area of the box is 432cm2.
(a) Express in terms of x:
(i) the internal height h, of the box; (3 marks)
(ii) the internal volume V, of the box. (1 mark)
(b) Find:
(i) the value of x for which the volume V is maximum; (4 marks)
(ii) the maximum internal volume of the box. (2 marks)
KCSE Mathematics Paper 2 2010
Searching for KCSE Mathematics Past papers? Find KCSE Mathematics Paper 2 2010. Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education Mathematics Paper 2 Past paper
SECTION 1 (50 MARKS)
1. The length and width of a rectangle measured to the nearest millimeter are 7.5cm and 5.2cm respectively. Find, to four significant figures, the percentage error in the area of the rectangle. (3 marks)
2. Simplify:
3. In the figure below, 0 is the centre of the circle which passes through the points T, C and D. Line TC is parallel to OD and line ATB is a tangent to the circle at T. Angle DOC = 36°.
Calculate the size of angle CTB. (3 marks)
4. A tea dealer mixes two brands of tea, x and y, to obtain 35kg of the mixture worth Ksh 62 per kg. If brand x is valued at Ksh 68 per kg and brand y at Ksh 53 per kg, calculate the ratio, in its simplest form, in which the brands x and y are mixed. (2 marks)
5. The length of a flower garden is 2m less than twice its width. The area of the garden is 60m2. Calculate its length. (3 marks)
6. Five people can build 3 huts in 21 days. Find the number of people, working at the same rate that will build 6 similar huts in 1 5 days. (2 marks)
7. When Ksh 40 000 was invested in a certain bank for 5 years it earned a simple interest of Ksh 3 800. Find the amount that must have been invested in the same bank at the same rate for 7 % years to earn a simple interest of Ksh 3 420. (3 marks)
8. The heights, in centimeters. of 100 tree seedlings are shown in the table below.
Find the quartile deviation of the heights. (4 marks)
9. A bag contains 2 white balls and 3 black balls. A second bag contains 3 whiteballs and 2 black balls. The balls are identical except for the colours. Two balls are drawn at random, one after the other from the first bag and placed in the second bag. Calculate the probability that the 2 balls are both white. (2 marks)
10. The points 0, A and B have the coordinates (0,0) (4,0) and (3,2) respectively. Under a shear represented by the matrix triangle OAB maps onto triangle OAB’.
(a) Determine in terms of k, the x coordinate of point B’. (2 marks)
(b) If OAB’ is a right angled triangle in which angle OB’A is acute, find two possible values of k. (2 marks)
11. A particle starts from 0 and moves in a straight line so that its velocity V ms-1 after t seconds is given by V = 3t – t2. The distance of the particle from 0 at time t seconds is F metres.
(a) Express s in terms of t and c where c is constant. (1 mark)
(b) Calculate the time taken before the particle returns to 0. (3 marks)
12.(a) Expand and simplify (2 – x)5. (2 marks)
(b) Use the first 4 terms of the expansion in part (a) above to find the approximate value of (1.8)5 to 2 decimal places. (2 marks)
13.(a) Using line AB given below, construct the locus of a point P such that ZAPB = 90°. (1 mark)
(b) On the same diagram locate two possible positions of point C such that point C is on the locus of P and is equidistant from A and B. (2 marks)
14. Make x the subject of the equation.
EQ
15. Find the value of x given that: log (15 – 5x) – 1 log (3x – 2) (3 marks)
16. The circle shown below cuts the x-axis at (-2,0) and (4,0). 4t also cuts y-axis at (0,2) and (0,-4)
Determine the:
(a) (i) coordinates of the centre (1 mark)
(ii) radius of the circle (1 mark)
(b) Equation of the circle in the form x2 + y2 + ax + by are constants. (2 marks)
17.(a) Complete the table below, giving the values correct to 2 decimal places.
(b) On the grid provided and using the same axes draw the graphs of y = coxs :x° and y = sin x° – cos x° for 0° < x < 180°. Use the scale 1 cm for 20° on the x-axis and 4cm for 1 unit on the y-axis. (5 marks)
(c) Using the graph in part (b):
(i) solve the equation sin x° – cos x° = 1.2 (1 mark)
(ii) solve the equation cos x0 = Vz sin x°; (1 mark)
(iii) determine the value of cos x° in part (c) (ii) above. (1 mark)
18. In the figure below OJKL is a parallelogram in which OJ = 3p and OL = 2r
(a) If A is a point on LK such that LA = 1/2AK and a point B divides the line JK externally in the ratio 3:1, express OB and AJ in terms of p and r. (2 marks)
(b) Line OB intersects AJ at X such that OX = mOB and AX = nAJ
(i) Express OX in terms of p, r and m. (1 mark)
(ii) Express OX in terms of p, r and n. (1 mark)
(iii) Determine the values of m and n and hence the ratio in which point X divides line AJ. (6 marks)
19. The positions of three ports A, B and C are (34°N, 16°W), (34°N, 24°E) and (26°S, 16°W) respectively.
(a) Find the distance in nautical miles between:
(i) Ports A and B to the nearest nautical miles; (3 marks)
(ii) Ports A and C. (2 marks)
(b) A ship left Port A on Monday at 1330h and sailed to Port B at 40 knots.
Calculate:
(i) the local time at Port B when the ship left Port A; (2 marks)
(ii) the day and the time the ship arrived at port B. (3 marks)
20. A carpenter takes 4 hours to make a stool and 6 hours to make a chair. It takes the carpenter and at least 144 hours to make x stools and y chairs. The labour cost of making a stool is Ksh 100 and that of a chair is Ksh 200. The total labour cost should not exceed Ksh 4 800. The carpenter must make at least 16 stools and more than 10 chairs.
(a) Write down inequalities to represent the above information. (3 marks)
(b) Draw the inequalities in (a) above on the grid provided.
(c) The carpenter makes a profit of Ksh 40 on a stool and Ksh 100 on a chair. Use the graph to determine the maximum profit the carpenter can make. (3 marks)
21. A hall can accommodate 600 chairs arranged in rows. Each row has the same number of chairs. The chairs are rearranged such that the number of rows are increased by 5 but the number of chairs per row is decreased by 6.
(a) Find the original number of rows of chairs in the hall. (6 marks)
(b) After the re-arrangement 450 people were seated in the hall leaving the same number of empty chairs in each row. Calculate the number of empty chairs per row. (4 marks)
22. The first term of an Arithmetic Progression (A.P.) with six terms is p and its common difference is c. Another A. P with five terms has also its first term as p and a common difference of d. The last terms of the two Arithmetic Progressions are equal.
(a) Express d in terms of c; (3 marks)
(b) Given that the 4th term of the second A.P. exceeds thp 4″1 tem of the first
one by 1 % , find the values of c and d. (3 marks)
(c) Calculate the value of p if the sum of the terms of the first A.P is 10 more
than the sum of the terms of the second A.P. (4 marks)
23. In a uniformity accelerated motion the distance, s metres, traveled ‘n time t seconds varies partly as the time and partly as the square of the time. When the time is 2 seconds, the distance traveled is 80 metres and when the time is 3 seconds, the distance traveled is 135 metres.
(a) Express s in terms of t. (5 marks)
(b) Find:
(i) the distance traveled in 5 seconds. (2 marks)
(ii) the time taken to travel a distance of 560 metres. (3 marks)
24. In the figure below, P, Q, R and S are points on the circle centre 0. PRT and USTV are straight lines. Line USTV is a tangent to the circle at S, ZRST = 50° and ZRTV = 150°.
(a) Calculate the size of:
(i) ORS;
(ii) USP;
(iii) PQR.
(b) Given that RT = 7cm and ST= 9cm, calculate to 3 significant figures:
(i) the length of line PR;
(ii) the radius of the circle.

Betty is a qualified teacher with a Bachelor of Education (Arts). In addition, she is a registered Certified Public Accountant. She has been teaching and offering part-time accounting services for the last 10 years. She is passionate about education, accounting, writing, and traveling.